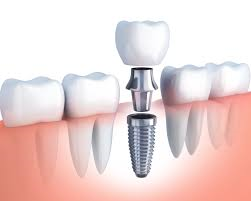
DENTAL IMPLANTS
What are Dental Implants? Dental implants are metal posts or frames that are surgically positioned into the jawbone beneath your gums. Once in place, they allow us to mount replacement teeth onto them.
- Endosteal implantsآ these are surgically implanted directly into the jawbone. Once the surrounding gum tissue has healed, a second surgery is needed to connect a post to the original implant. Finally, an artificial tooth (or teeth) is attached to the post-individually, or grouped on a bridge or denture.
- Subperiosteal implantsآ these consist of a metal frame that is fitted onto the jawbone just below the gum tissue. As the gums heal, the frame becomes fixed to the jawbone. Posts, which are attached to the frame, protrude through the gums. As with endosteal implants, artificial teeth are then mounted to the posts.
A typical conventional implant consists of a titanium screw (resembling a tooth root) with a roughened or smooth surface. The majority of dental implants are made of commercially pure titanium, which is available in four grades depending upon the amount of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and iron contained.Cold work hardened CP4 (maximum impurity limits of N .05 percent, C .10 percent, H .015 percent, Fe .50 percent, and O .40 percent) is the most commonly used titanium for implants. Grade 5 titanium, Titanium 6AL-4V (signifying the titanium alloy containing 6 percent aluminium and 4 percent vanadium alloy) is slightly harder than CP4 and used in the industry mostly for abutment screws and abutments.Most modern dental implants also have a textured surface (through etching, anodic oxidation or various-media blasting) to increase the surface area and osseointegrationpotential of the implant.: If C.P. titanium or a titanium alloy has more than 85% titanium content, it will form a titanium-biocompatible titanium oxidesurface layer or veneer that encloses the other metals, preventing them from contacting the bone.Ceramic (zirconia-based) implants exist in one-piece (combining the screw and the abutment) or two-piece systems – the abutment being either cemented or screwed – and might lower the risk for peri‐implant diseases, but long-term data on success rates is missing. Hard tissue (bone) reconstruction
Main articles: Sinus liftBone grafting is necessary when there is a lack of bone. Also, it helps to stabilize the implant by increasing survival of the implant and decreasing marginal bone level loss.While there are always new implant types, such as short implants, and techniques to allow compromise, a general treatment goal is to have a minimum of 10 mm in bone height, and 6 mm in width. Alternatively, bone defects are graded from A to D (A=10+ mm of bone, B=7–9 mm, C=4–6 mm and D=0–3 mm) where an implant’s likelihood of osseointegrating is related to the grade of bone. To achieve an adequate width and height of bone, various bone grafting techniques have been developed. The most frequently used is called guided bone graft augmentation where a defect is filled with either natural (harvested or autograft) bone or allograft (donor bone or synthetic bone substitute), covered with a semi-permeable membrane and allowed to heal. During the healing phase, natural bone replaces the graft forming a new bony base for the implant. Three common procedures are:- Sinus lift
- Lateral alveolar augmentation (increase in the width of a site)
- Vertical alveolar augmentation (increase in the height of a site)
زراعه الاسنان
ما هي زراعة الأسنان؟
زراعة الأسنان عبارة عن أعمدة أو إطارات معدنية يتم وضعها جراحيًا في عظم الفك أسفل اللثة. بمجرد وضعها في مكانها، فإنها تسمح لنا بتركيب الأسنان البديلة عليها.
- الزراعات المبطنة: يتم زرعها جراحيًا مباشرة في عظم الفك. بمجرد شفاء أنسجة اللثة المحيطة، يلزم إجراء عملية جراحية ثانية لربط عمود الزرع الأصلي. وأخيرًا، يتم ربط سن صناعي (أو أسنان) بالجزء الخلفي بشكل فردي أو تجميعه على جسر أو طقم أسنان.
- الزراعات تحت العظام: تتكون من إطار معدني يتم تركيبه على عظم الفك أسفل أنسجة اللثة مباشرة. ومع شفاء اللثة، يصبح الإطار ثابتًا على عظم الفك. تبرز الأعمدة المرتبطة بالإطار من خلال اللثة. كما هو الحال مع زراعة بطانة العظم، يتم بعد ذلك تركيب الأسنان الاصطناعية على الأعمدة.
- تتكون الزراعه التقليدية النموذجية من برغي من التيتانيوم (يشبه جذر السن) بسطح خشن أو أملس. غالبية زراعة الأسنان مصنوعة من التيتانيوم النقي تجاريًا، وهو متوفر في أربع درجات اعتمادًا على كمية الكربون والنيتروجين والأكسجين والحديد الموجودة. يعتبر CP4 المقسى بالعمل البارد (حدود الشوائب القصوى N .05 بالمائة، C .10 بالمائة، H .015 بالمائة، Fe .50 بالمائة، وO .40 بالمائة) هو التيتانيوم الأكثر استخدامًا في عمليات الزرع. التيتانيوم من الدرجة 5، التيتانيوم 6AL-4V (يشير إلى سبائك التيتانيوم التي تحتوي على 6 بالمائة من الألومنيوم و4 بالمائة من سبائك الفاناديوم) أصعب قليلًا من CP4 ويستخدم في الصناعة في الغالب للبراغي والدعامات. تحتوي معظم زراعة الأسنان الحديثة أيضًا على سطح محكم (من خلال النقش أو الأكسدة الأنودية أو تفجير الوسائط المختلفة) لزيادة مساحة السطح وإمكانية التكامل العظمي للزرعة: إذا كان التيتانيوم أو سبائك التيتانيوم تحتوي على أكثر من 85 بالمائة من محتوى التيتانيوم، فإنها ستشكل طبقة سطحية من أكسيد التيتانيوم المتوافق حيويًا أو قشرة تحيط بالمعادن الأخرى، مما يمنعها من ملامسة العظام. توجد الغرسات الخزفية (المعتمدة على الزركونيا) في قطعة واحدة (تجمع بين المسمار والدعامة) أو أنظمة من قطعتين – الدعامة إما مثبتة أو مثبتة بالبراغي – وقد تقلل من خطر الإصابة بالأمراض المحيطة بالزرع، ولكن البيانات طويلة المدى حول معدلات النجاح مفقودة.
إعادة بناء الأنسجة الصلبة (العظام).
المقالات الرئيسية: رفع الجيوب الأنفية
تطعيم العظام ضروري عندما يكون هناك نقص في العظام. كما أنه يساعد على تثبيت الزرعة عن طريق زيادة بقاء الزرعة وتقليل فقدان مستوى العظام الهامشية. في حين أن هناك دائمًا أنواع جديدة من الغرسات، مثل الغرسات القصيرة، وتقنيات تسمح بالتسوية، فإن الهدف العام للعلاج هو أن يكون ارتفاع العظام 10 ملم على الأقل، وعرضها 6 ملم. وبدلاً من ذلك، يتم تصنيف عيوب العظام من A إلى D (A = 10 مم من العظام، B = 7-9 مم، C = 4-6 مم، D = 0-3 مم) حيث يرتبط احتمال التكامل العظمي في الغرسة بدرجة العظام.
لتحقيق العرض والارتفاع المناسبين للعظام، تم تطوير تقنيات مختلفة لتطعيم العظام. الطريقة الأكثر استخدامًا تسمى تكبير الطعم العظمي الموجه حيث يتم ملء العيب إما بالعظم الطبيعي (المحصود أو الطعم الذاتي) أو الطعم الخيفي (عظم متبرع أو بديل عظم صناعي)، مغطى بغشاء شبه منفذ ويسمح له بالشفاء. خلال مرحلة الشفاء، يحل العظم الطبيعي محل الطعوم مشكلاً قاعدة عظمية جديدة للزرعة.
ثلاثة إجراءات شائعة هي:
1. رفع الجيوب الأنفية
2. تكبير الحويصلات الهوائية الجانبية (زيادة عرض الموقع)
3. تكبير السنخية العمودية (زيادة ارتفاع الموقع)
توجد أيضًا إجراءات أكثر تدخلاً لعيوب العظام الأكبر حجمًا، بما في ذلك تعبئة العصب السنخي السفلي للسماح بوضع أداة تثبيت، أو تطعيم العظام باستخدام العرف الحرقفي أو مصدر كبير آخر للعظم وطعم العظام والأوعية الدموية الدقيقة حيث يتم زرع إمدادات الدم إلى العظام.
زراعة الأسنان هي حل ثابت لتعويض الأسنان المفقودة باستخدام جذور صناعية من التيتانيوم وتيجان تشبه الأسنان الطبيعية، لاستعادة المضغ والابتسامة بثقة … احجز الآن